How to operate a drone? This seemingly simple question opens a world of exciting possibilities, from breathtaking aerial photography to precision surveying. Mastering drone operation requires a blend of technical skill and responsible awareness. This guide will equip you with the knowledge and confidence to safely and effectively pilot your drone, covering everything from pre-flight checks to advanced flight maneuvers and troubleshooting common issues.
We’ll explore the intricacies of drone controls, camera operation, battery management, and maintenance, ensuring you can capture stunning visuals and enjoy the thrill of flight responsibly.
We’ll delve into the essential steps of pre-flight preparation, emphasizing safety protocols and legal compliance. You’ll learn how to navigate your drone using various control methods, optimize camera settings for exceptional image quality, and effectively manage battery life for extended flight times. We’ll also address potential problems and their solutions, guiding you through troubleshooting and maintenance procedures to keep your drone in top condition.
Pre-Flight Checklist and Safety Procedures

Before embarking on any drone flight, a comprehensive pre-flight checklist is crucial for ensuring safe and successful operation. This involves a thorough inspection of the drone’s components, understanding local regulations, and practicing a safe takeoff and landing procedure. Neglecting these steps can lead to accidents, damage to property, or even injury.
Drone Pre-Flight Inspection
A meticulous pre-flight inspection is paramount to prevent mid-flight malfunctions. This involves visually checking all major components for any signs of damage or wear. The following table Artikels a systematic approach:
| Propellers | Battery | GPS | Camera |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inspect for cracks, chips, or bends. Ensure they are securely fastened. | Check battery level and ensure it’s fully charged. Inspect for any physical damage. | Confirm GPS signal is strong and accurate. Allow sufficient time for satellite acquisition. | Verify camera lens is clean and free of obstructions. Check SD card capacity. |
| Replace damaged propellers immediately. | Use only manufacturer-approved batteries. Avoid overcharging. | If GPS signal is weak, relocate to an area with better reception. | Test camera functionality by taking a test photo or video. |
Understanding Local Regulations and Airspace Restrictions
Operating a drone responsibly requires adhering to all applicable local, state, and federal regulations. These regulations often dictate where and when you can fly, as well as restrictions on altitude and proximity to people and infrastructure. Failing to comply can result in fines or legal repercussions. Websites like the FAA’s B4UFLY app (in the US) or similar national aviation authorities provide crucial information on airspace restrictions.
Safe Takeoff and Landing Procedures

Safe takeoff and landing are critical for preventing accidents. A smooth, controlled ascent and descent minimizes the risk of damage to the drone or its surroundings. Here’s a recommended procedure:
- Select a clear, open area away from obstacles and people.
- Power on the drone and controller, ensuring a strong GPS signal.
- Perform a pre-flight calibration if necessary (consult your drone’s manual).
- Slowly and gently lift the drone into the air, maintaining a steady ascent.
- For landing, gradually descend the drone, keeping it level and stable.
- Power off the drone and controller after landing.
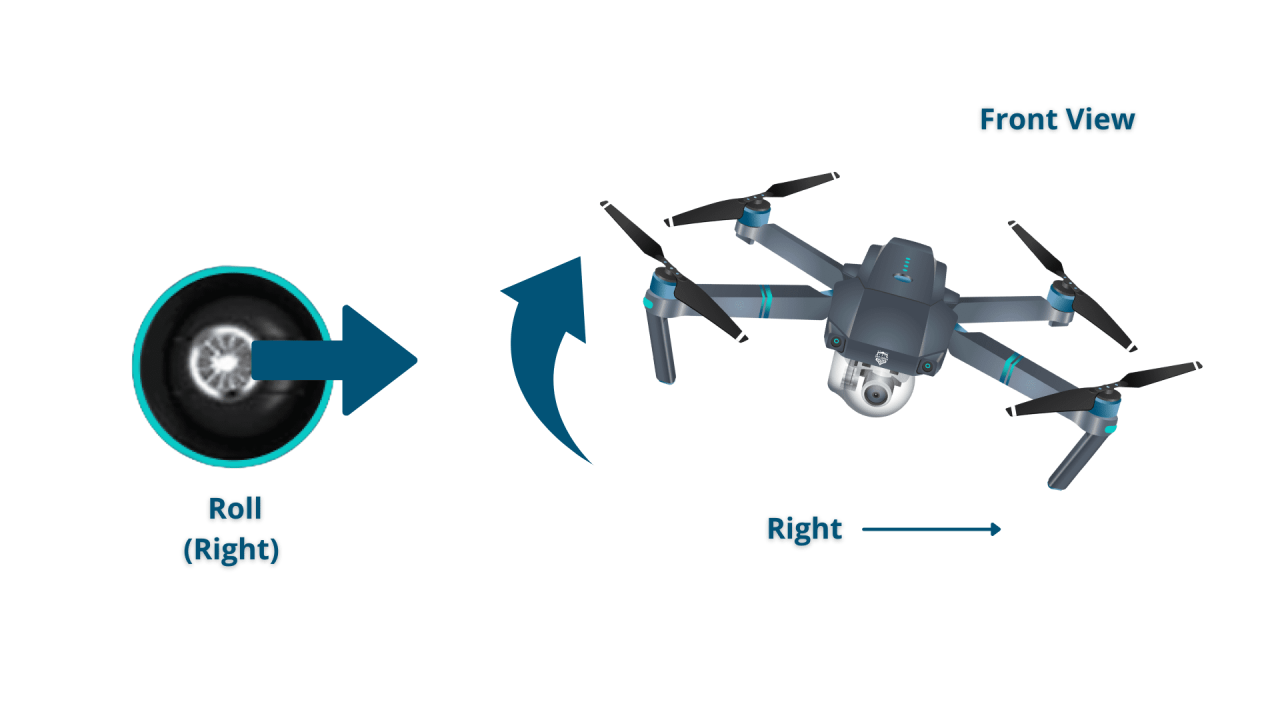
Drone Controls and Navigation
Understanding your drone’s controls is fundamental to safe and effective operation. Different drones may have slightly varying controls, but the core functionalities remain consistent. Furthermore, mastering various flight modes enhances your ability to navigate diverse environments and capture dynamic shots.
Drone Control Stick Functions
Most drone controllers utilize two joysticks for controlling the drone’s movement. The functions typically include:
- Left Stick: Controls altitude and yaw (rotation).
- Right Stick: Controls pitch (forward/backward) and roll (left/right).
- Buttons: Various buttons control camera functions, flight modes, return-to-home, and emergency stops.
Drone Flight Modes, How to operate a drone
Different flight modes cater to varying skill levels and flight situations. Beginner mode limits speed and responsiveness, providing a safer experience for novices. Sport mode allows for faster and more agile maneuvers, while GPS mode enhances stability and precision. Understanding these modes is crucial for adapting to different conditions.
GPS Navigation and Waypoints
Many drones utilize GPS for precise positioning and navigation. This allows you to set waypoints, creating pre-programmed flight paths. For example, imagine you want to film a scenic route. You could program waypoints along the route, and the drone will autonomously follow the path, capturing footage from pre-determined positions.
Camera Operation and Image Capture
The camera is a key feature of many drones, allowing for stunning aerial photography and videography. Mastering camera settings and composition techniques will significantly enhance the quality and visual appeal of your captured media.
Adjusting Camera Settings
Camera settings like ISO, shutter speed, and aperture directly impact image quality. In bright sunlight, a lower ISO and faster shutter speed are generally preferred to prevent overexposure. In low-light conditions, a higher ISO and slower shutter speed might be necessary, though this can introduce noise. Aperture control affects depth of field, influencing background blur.
Capturing Photos and Videos
The process of capturing photos and videos varies slightly depending on the drone model. However, most drones provide dedicated buttons or on-screen controls for starting and stopping recordings. Many drones allow for simultaneous photo and video capture. Always ensure sufficient storage space on your SD card.
Composing Shots
Effective composition enhances the visual impact of your aerial footage. Experiment with different angles, perspectives, and framing techniques. Consider the rule of thirds, leading lines, and other compositional guidelines to create visually appealing and dynamic shots. A bird’s-eye view can provide a unique perspective, while lower angles can create a sense of scale and depth.
Battery Management and Flight Time: How To Operate A Drone
Proper battery management is crucial for extending the lifespan of your drone batteries and ensuring sufficient flight time. Understanding the factors that influence flight time allows for better planning and prevents unexpected power outages during flights.
Best Practices for Battery Management
Always use manufacturer-recommended chargers and avoid overcharging. Store batteries in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight. Avoid completely depleting batteries, as this can reduce their lifespan. Regularly inspect batteries for any signs of damage or swelling.
Factors Affecting Flight Time
Several factors influence flight time. Weather conditions, such as strong winds or extreme temperatures, can significantly reduce flight time. Heavier payloads (cameras, accessories) also decrease flight time. Aggressive flight maneuvers consume more battery power than gentle, steady flights.
Battery Management Schedule
For multiple flights, a simple schedule can optimize battery usage. For example: Flight 1: Battery 1; Flight 2: Battery 2; Flight 3: Battery 1 (while Battery 2 charges); Flight 4: Battery 2; etc. This ensures you always have a charged battery ready for your next flight.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Successfully navigating these steps requires practice and a good understanding of safety regulations. For a comprehensive guide covering everything from basic controls to advanced maneuvers, check out this helpful resource on how to operate a drone. This resource will ensure you’re well-prepared before your next flight, enhancing your drone piloting skills.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Even with careful preparation, drone malfunctions can occur. Knowing how to troubleshoot common issues can save you time and prevent more serious problems. This section Artikels common problems and their solutions, guiding you through a systematic troubleshooting process.
Successfully piloting a drone involves understanding its controls and mastering basic flight maneuvers. Learning the fundamentals is crucial before attempting more complex operations; for a comprehensive guide, check out this helpful resource on how to operate a drone which covers everything from pre-flight checks to advanced techniques. Safe and responsible drone operation requires consistent practice and a thorough understanding of the regulations involved.
Common Drone Malfunctions and Solutions
Here’s a flowchart-style guide for troubleshooting:
- Issue: GPS signal loss. Solution: Relocate to an area with better GPS reception; ensure clear sky visibility.
- Issue: Low battery. Solution: Land the drone immediately; charge the battery.
- Issue: Propeller damage. Solution: Replace the damaged propeller; inspect other propellers for damage.
- Issue: Drone unresponsive. Solution: Try restarting the drone and controller; check battery connections; if the problem persists, seek professional assistance.
- Issue: Camera malfunction. Solution: Check camera settings; ensure SD card is properly inserted and has sufficient space; if the issue persists, seek professional assistance.
Drone Maintenance and Cleaning
Regular maintenance and cleaning are essential for ensuring your drone’s optimal performance and longevity. This involves routine cleaning, proper storage, and regular inspections for wear and tear.
Cleaning and Maintenance
After each flight, gently clean the drone’s body and propellers using a soft cloth and mild cleaning solution. Avoid using harsh chemicals or abrasive materials. Regularly inspect the drone’s gimbal and camera lens for dirt or debris. Keep all moving parts lubricated as recommended by the manufacturer.
Proper Storage
Store the drone in a cool, dry, and safe location away from direct sunlight and extreme temperatures. Keep the drone and its accessories in their designated cases or containers to prevent damage. Always store batteries separately and according to manufacturer guidelines.
Inspecting for Wear and Tear
Regularly inspect the drone for signs of wear and tear. Pay close attention to the propellers, motors, landing gear, and camera gimbal. Check for cracks, loose screws, or any signs of damage. If you notice any significant wear, replace or repair the affected components as needed.
Operating a drone is a rewarding experience, combining technology, skill, and creativity. By following the guidelines Artikeld in this guide, you’ll be well-prepared to safely and effectively pilot your drone, capturing stunning visuals and exploring the exciting possibilities of aerial technology. Remember, responsible drone operation is key to ensuring both your safety and the safety of others. Continue practicing and expanding your skills to unlock the full potential of your drone.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the legal age to operate a drone?
Legal age varies by location and drone type. Check local regulations.
How do I register my drone?
Registration requirements depend on your location and drone weight. Check your country’s aviation authority website.
What should I do if I lose GPS signal?
Immediately switch to a lower flight mode (like Beginner mode) and carefully maneuver the drone back to your location using visual cues.
How often should I calibrate my drone’s compass?
Calibrate your compass before each flight, especially if you’ve moved to a new location or experienced any interference.